
The Sabertooth 2X25 is a dual motor driver. It is suitable for high powered robots - up to 100lbs in combat or 300lbs for general purpose robotics.
Out of the box, the Sabertooth can supply two DC brushed motors with up to 25A each. Peak currents of 50A per channel are achievable for a few seconds.
.png)

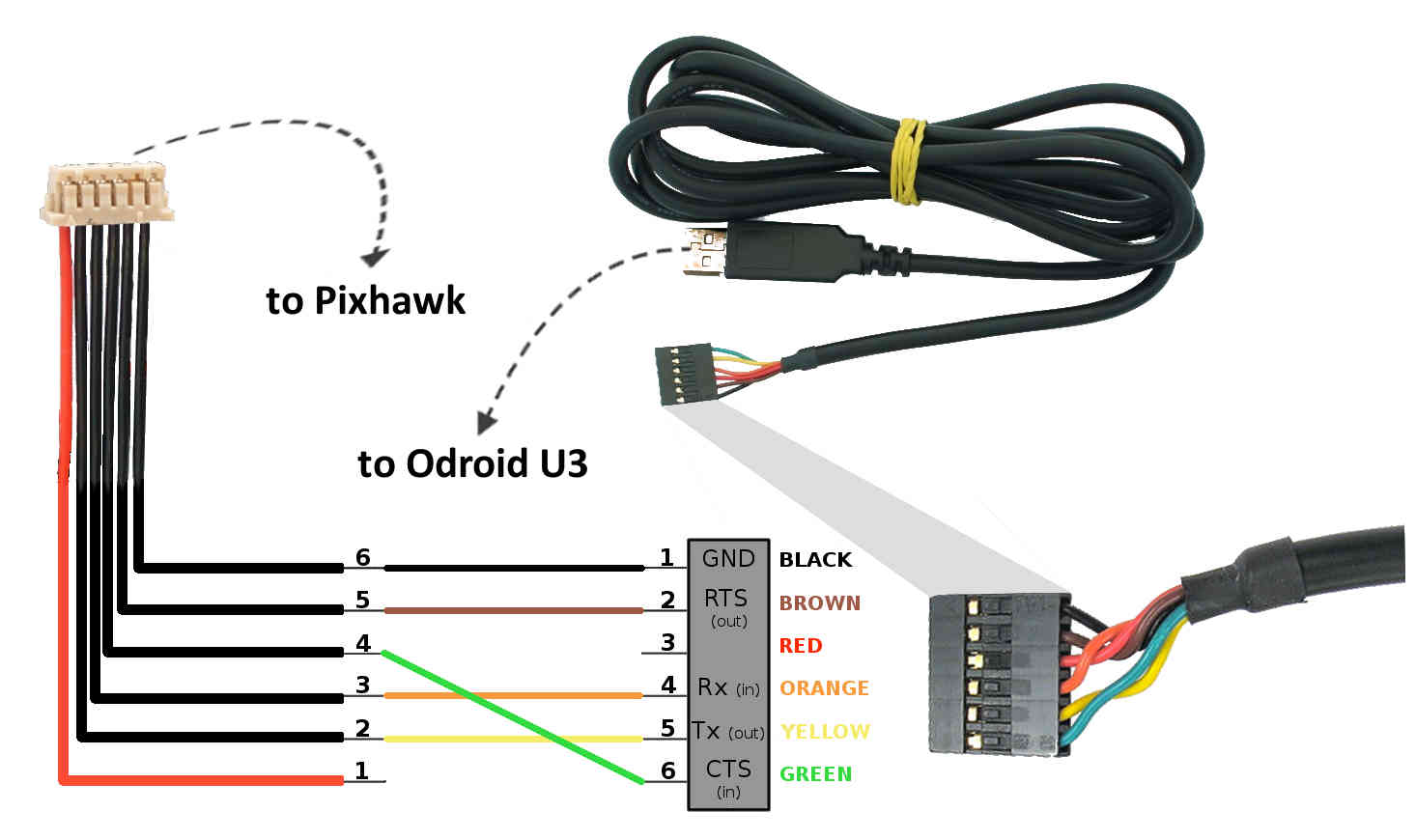
FTDI cable from Computer to Sabertooth is all that is needed.
References
- Specs
- Quick Start Guide
- User Manual
- Packtized Serial
- Addresses for Packetized Mode
